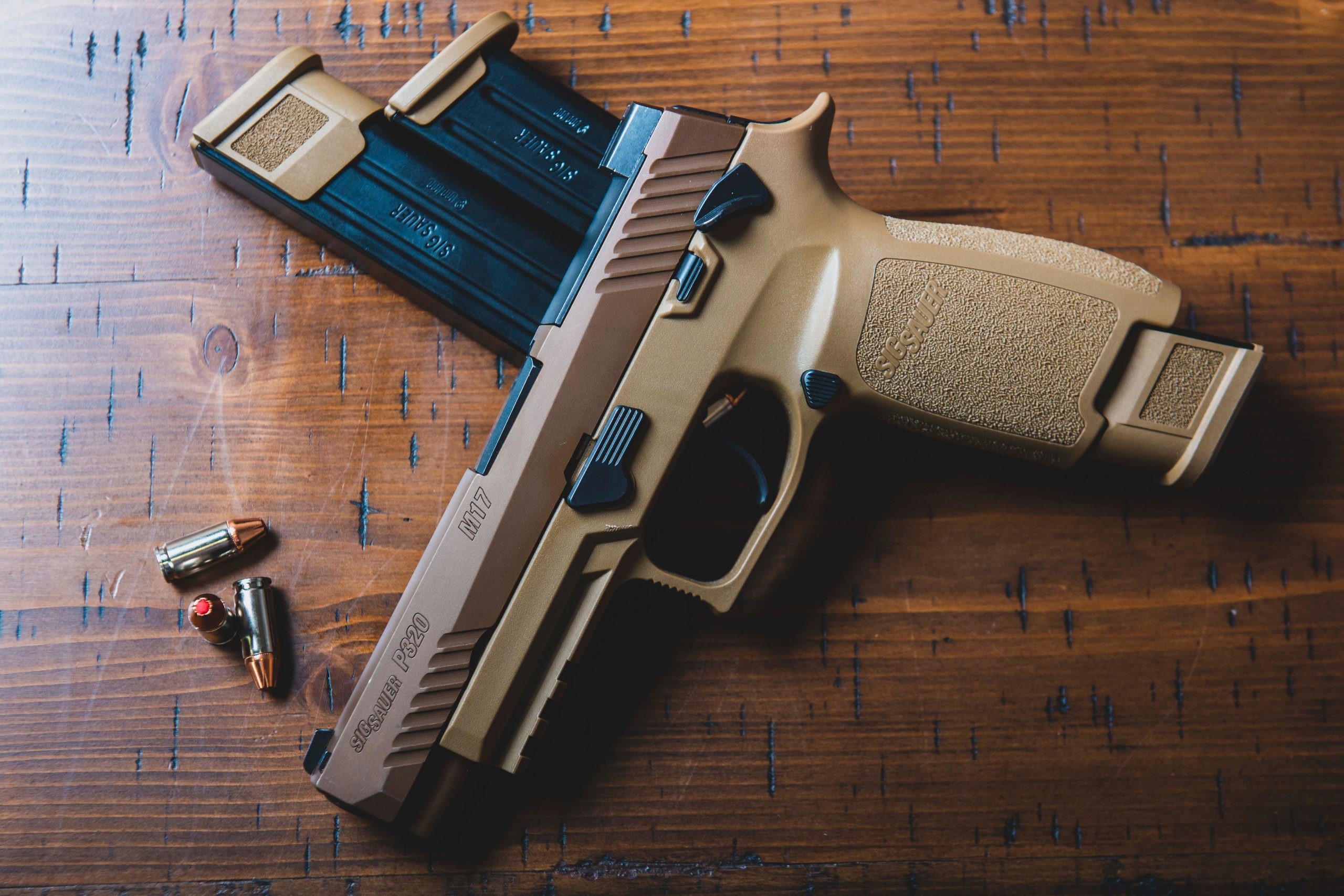
Shooting ranges are popular in Texas, but anytime someone handles a gun there is a risk for injury. Despite the safety procedures in place in most Texas ranges, accidents do occur, and individuals are sometimes shot, leading to injuries or even death. Like most accidents, Texas law allows victims to file a civil negligence suit to recover for their injuries against a negligent party who caused the accident. However, the requirements for filing a lawsuit against a shooting range are a bit more complicated, meaning some plaintiffs who misunderstand the statutory requirements for filing may have their suit dismissed regardless of its merits.
Shooting ranges are popular in Texas, but anytime someone handles a gun there is a risk for injury. Despite the safety procedures in place in most Texas ranges, accidents do occur, and individuals are sometimes shot, leading to injuries or even death. Like most accidents, Texas law allows victims to file a civil negligence suit to recover for their injuries against a negligent party who caused the accident. However, the requirements for filing a lawsuit against a shooting range are a bit more complicated, meaning some plaintiffs who misunderstand the statutory requirements for filing may have their suit dismissed regardless of its merits.
The Supreme Court of Texas recently considered a case that highlights these requirements. According to the written opinion, the plaintiff brought his loaded .22 caliber rifle to the defendant shooting range in December of 2016. He handed the gun to a range employee for a pre-entrance safety inspection, and during the inspection, the gun discharged and shot the plaintiff in the leg. As a result, the plaintiff suffered severe injuries that required extensive medical treatment.
In February of 2017, the plaintiff sued the shooting range and the employee who performed the inspection. The parties submitted an agreed-upon scheduling order, which was approved in April. The order provided a date by which all experts must be designated. In June of 2017, more than 90 days after the suit was filed, the defendants filed a motion to dismiss, based on section 128.053 of the Texas Civil Practice and Remedies Code. This section requires that a plaintiff suing a shooting range must serve an expert report on the defendants within 90 days of the original filing, unless that deadline is extended by written agreement. If a plaintiff fails to do so, their suit can be dismissed with prejudice. The defendants argued that the plaintiffs had not served them with an expert witness within 90 days, and thus the suit must be dismissed. The plaintiffs, on the other hand, argued that the scheduling order extended the deadline, even though it did not mention section 128.053.
 Texas Injury Lawyers Blog
Texas Injury Lawyers Blog


 Many Texans spend the majority of their time at work. As a result, San Antonio
Many Texans spend the majority of their time at work. As a result, San Antonio  Under Texas premises liability law, restaurants and bars have a duty to protect their customers. However, the extent of this duty is often called into question in cases where someone is injured while visiting an eating or drinking establishment. In a recent
Under Texas premises liability law, restaurants and bars have a duty to protect their customers. However, the extent of this duty is often called into question in cases where someone is injured while visiting an eating or drinking establishment. In a recent  Shooting ranges are popular in Texas, but anytime someone handles a gun there is a risk for injury. Despite the safety procedures in place in most Texas ranges, accidents do occur, and individuals are sometimes shot, leading to injuries or even death. Like most accidents, Texas law allows victims to file a civil negligence suit to recover for their injuries against a negligent party who caused the accident. However, the requirements for filing a lawsuit against a shooting range are a bit more complicated, meaning some plaintiffs who misunderstand the statutory requirements for filing may have their suit dismissed regardless of its merits.
Shooting ranges are popular in Texas, but anytime someone handles a gun there is a risk for injury. Despite the safety procedures in place in most Texas ranges, accidents do occur, and individuals are sometimes shot, leading to injuries or even death. Like most accidents, Texas law allows victims to file a civil negligence suit to recover for their injuries against a negligent party who caused the accident. However, the requirements for filing a lawsuit against a shooting range are a bit more complicated, meaning some plaintiffs who misunderstand the statutory requirements for filing may have their suit dismissed regardless of its merits.